The first wall is the core component of the ITER device and is located in the annular vacuum chamber. Directly facing plasma at hundreds of millions of degrees Celsius during operation, it protects peripheral components and equipment from high heat flow and high-energy particle flow. According to the different levels of heat load on the surface, the first wall of ITER is divided into ordinary heat load type and enhanced heat load type. SWIP undertakes about 10% of the production and manufacturing task for the enhanced thermal load type components.
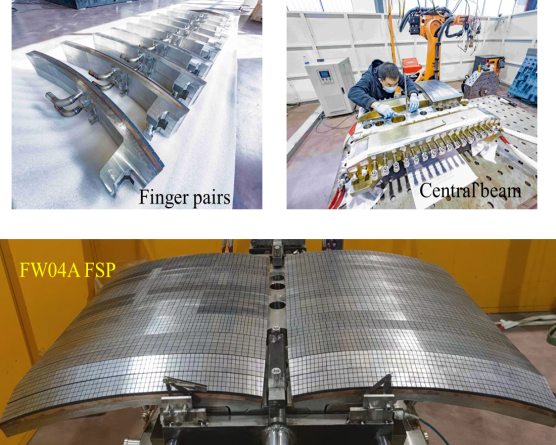
The full-size prototype of the enhanced-heat-flux (EHF) first wall (FW) panel, has been completed in China with its core indexes being significantly better than its design requirements and meeting the conditions for mass manufacturing, marking a new breakthrough by China in the scientific research of the core technology of EHF FW.
The EHF FW panel, which can withstand a surface plasma ion temperature of the reactor core up to 150 million C, some 10 times hotter than the real Sun, during the operation of the ITER, is the most critical core component of the reactor, involving the core technology of the fusion reactor construction.
The full-size prototype piece of the ITER EHF FW was developed, by SWIP, in China.
Based on this technology, the international standard "Reactor technology - Nuclear fusion reactors - Hot helium leak testing method for high temperature pressure-bearing components in nuclear fusion reactors" (standard number: ISO 4233:2023), was officially released in 2023.